Create and Write Lambda Functions
Create and Write Lambda Functions
In this step, we will create a data table in DynamoDb.
- Use the search bar to find the Lambda service, go to Function, and select Create Function.
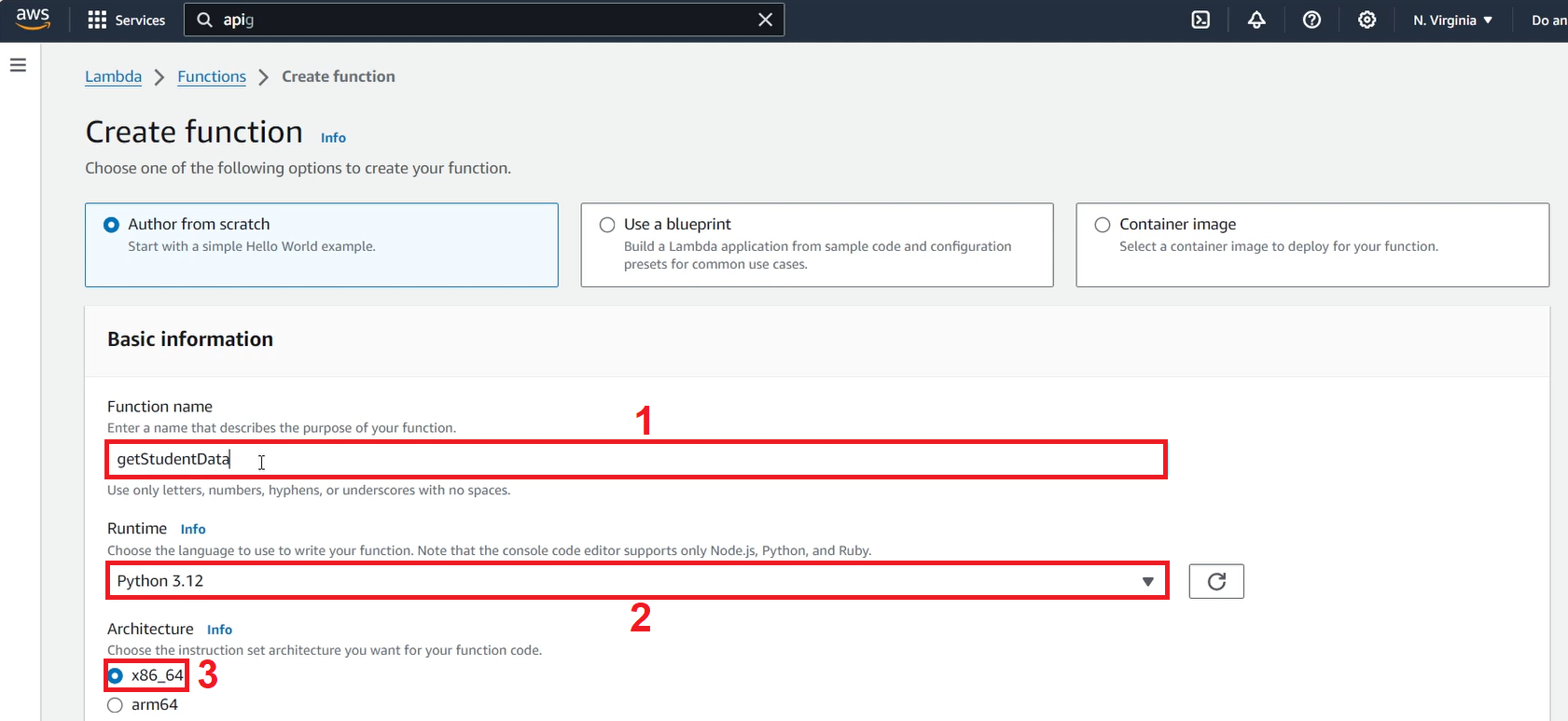
- Name the function, set the Runtime to Python 3.12, and Architecture to x86_64.
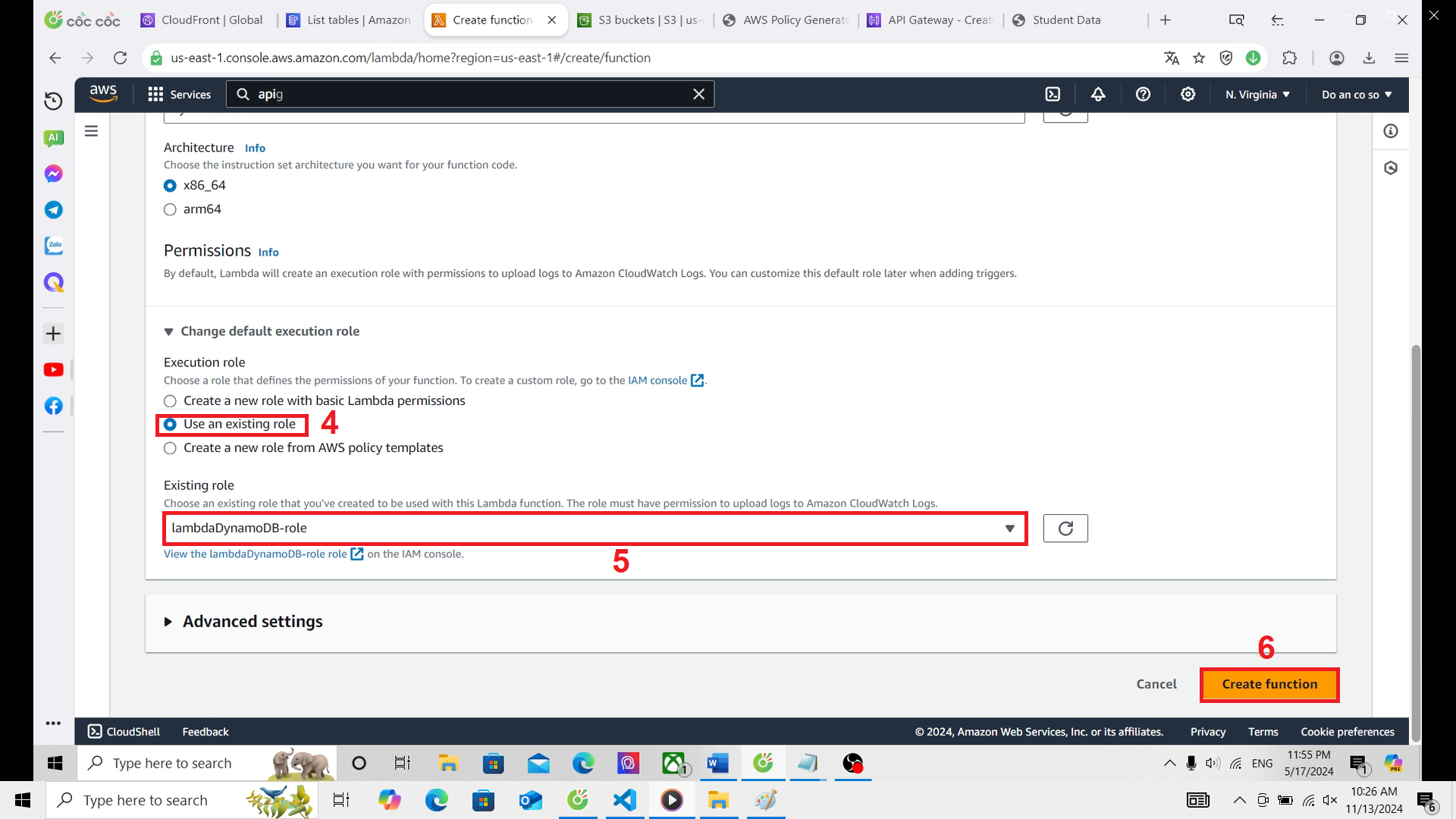
- In the Permission section, choose Use an existing role, and select the role you created in step 2.1.
- After creating the function, wait for the code editor to be set up.
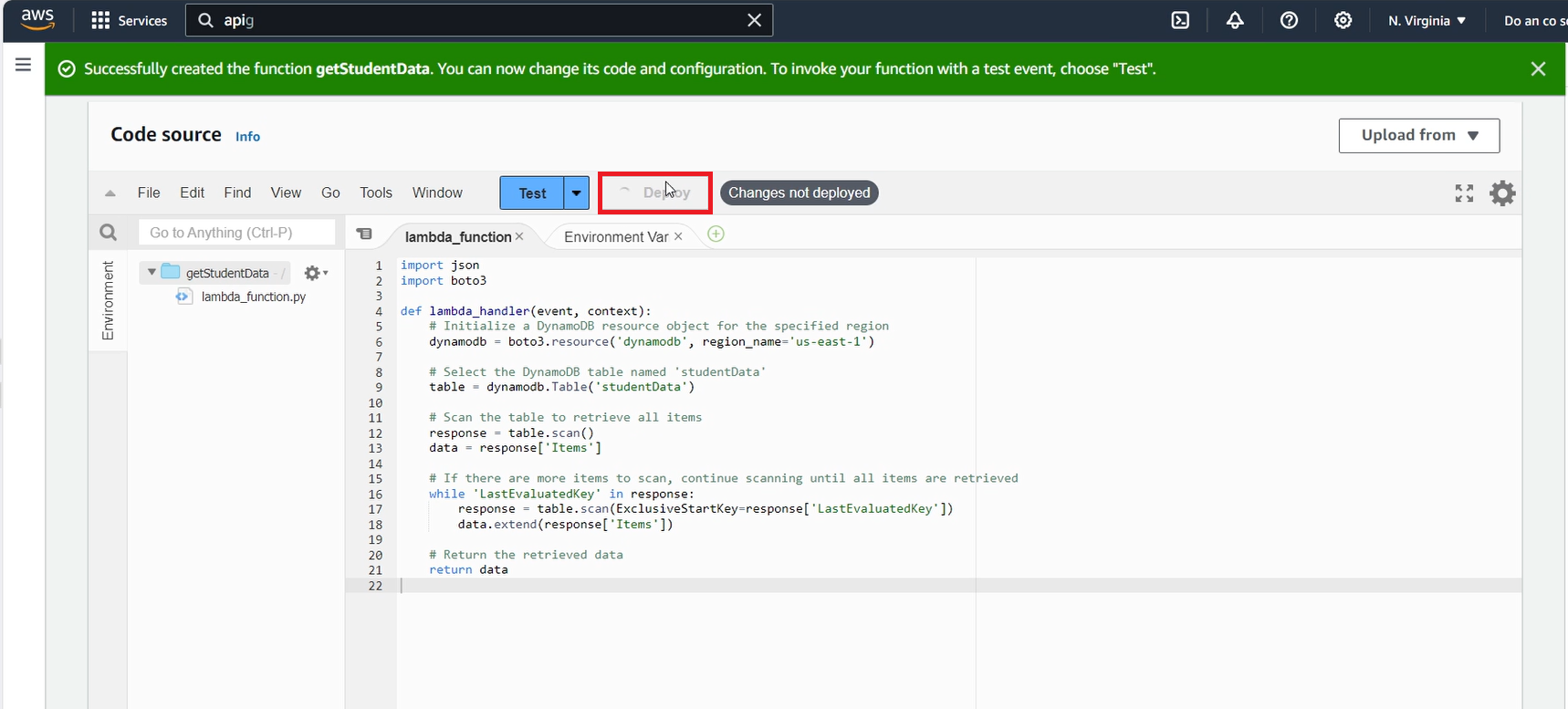
- Write the code for the getStudentData function as follows:
import json
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Initialize a DynamoDB resource object for the specified region
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb', region_name='us-east-1')
# Select the DynamoDB table named 'studentData'
table = dynamodb.Table('studentData')
# Scan the table to retrieve all items
response = table.scan()
data = response['Items']
# If there are more items to scan, continue scanning until all items are retrieved
while 'LastEvaluatedKey' in response:
response = table.scan(ExclusiveStartKey=response['LastEvaluatedKey'])
data.extend(response['Items'])
# Return the retrieved data
return data
In the line dynamodb = boto3.resource(‘dynamodb’, region_name=‘us-east-1’), replace us-east-1 with the region where your AWS account is located. My account is in the N. Virginia region, so I use us-east-1. After adjusting, click Deploy to deploy the function.
- Repeat steps 1 to 4 to create another function named insertStudentData, and use the following code:
import json
import boto3
# Create a DynamoDB object using the AWS SDK
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
# Use the DynamoDB object to select our table
table = dynamodb.Table('studentData')
# Define the handler function that the Lambda service will use as an entry point
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Extract values from the event object we got from the Lambda service and store in variables
student_id = event['studentid']
name = event['name']
student_class = event['class']
age = event['age']
# Write student data to the DynamoDB table and save the response in a variable
response = table.put_item(
Item={
'studentid': student_id,
'name': name,
'class': student_class,
'age': age
}
)
# Return a properly formatted JSON object
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps('Student data saved successfully!')
}